Rhadamanthys has emerged as a sophisticated tool for data theft, initially announced in underground chatting platforms in September 2022. It has quickly transitioned into a full-fledged commercial malware-as-a-service, making waves in cybercrime circles.
Recent observations of the actor’s activities on their Tor storefront and Telegram channels reveal a clear marketing strategy, featuring tiered subscription options priced from $299 to $499 per month. This enhancement in their sales framework not only highlights the technical advancement of Rhadamanthys but also reflects the developers’ commitment to establishing a long-lasting enterprise.
Rhadamanthys: Professionalization and Pricing Tiers
The newly designed Tor site is branded under RHAD Security and Mythical Origin Labs, showcasing a user-friendly interface that delineates the various offerings, version updates, and customer support options available. The “Basic” package, available for $299 monthly, is a self-hosted version, while the “Pro” tier at $499 includes added features like a rented server and enhanced security measures such as two-factor authentication, priority updates, and customizable hook configurations.
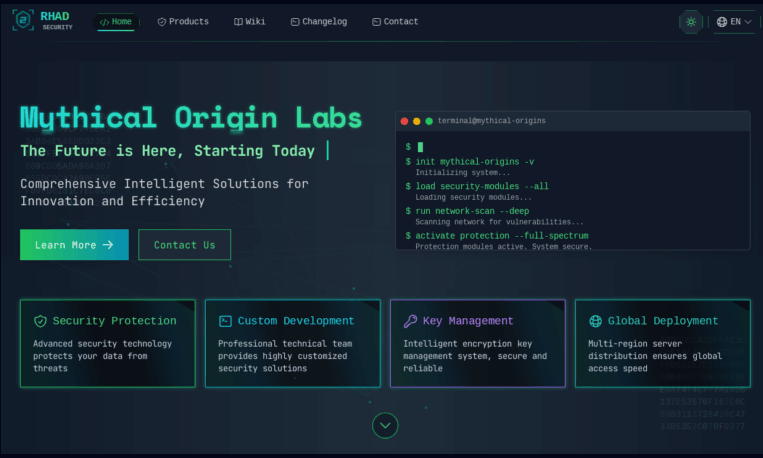
In addition to the fixed packages, an “Enterprise” option is available through individual negotiation. The site also features a “Version History” section which, despite sometimes lagging in updates, provides insights into incremental enhancements such as improved database structure, enhanced client-side injection capabilities, and the removal of registry write operations for increased stealth.
Latest Technical Upgrades in Version 0.9.x
The recent v0.9.2 update introduces critical technical modifications that alter the landscape for defenders, necessitating updates to analysis tools. The custom module container formats have transitioned from XS1 and XS2 to XS1B and XS2B. Notably, XS1B introduces a version field in its header while simplifying import-table deobfuscation, cutting down the import key to a single byte. XS2B expands a custom import field from WORD to DWORD, potentially rendering older parsers ineffective.
Additionally, string obfuscation in Stage 3 has undergone a complete overhaul, switching from an XOR-based encryption to an RC4 method to thwart signature-based extraction efforts. The primary loader for Rhadamanthys now features a Lumma-style message box during execution, mimicking the behavior of other infostealers while utilizing Win32 API calls instead of raw syscalls.
The evasion module in Stage 2 has also seen upgrades, enabling the dynamic loading of multiple configuration fragments. This allows for comprehensive environmental checks, leveraging UUIDv1 and WQL queries for MAC-address and HWID filtering, as well as detecting sandbox-specific elements like wallpapers and dummy files. The removal of the registry-based re-execution delay and the integration of a 16-byte seed hashed with “XRHY” for mutex generation serve to complicate universal vaccination attempts.
Communications with the command-and-control (C2) server now securely utilize WebSocket over TLS but have replaced the Stage 3 payload with raw PNG pixel data instead of wav or jpeg files for steganography. The new PNG header combines a 32-byte key along with the payload size, hash, and data array, simplifying the delivery despite a slight reduction in covert methods.
Before establishing a connection, Rhadamanthys queries multiple NTP servers to verify system time; simultaneously, a pseudo-random string routine partially obscures the C2 domain in memory. Although this distraction does not significantly impede connectivity, it showcases the increasingly sophisticated nature of its operation. Analysts are advised to adapt configuration parsers for the new 0xBEEF marker, update XS-format tools, and prioritize monitoring for the new PNG-based payload delivery methods. Rhadamanthys continues to represent a significant challenge within the information stealer ecosystem.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
For those tracking Rhadamanthys, the following analyzed samples have been identified:
- 8f54612f441c4a18564e6badf5709544370715e4529518d04b402dcd7f11b0fb (packed, Golang packer)
- b429a3e21a3ee5ac7be86739985009647f570548b4f04d4256139bc280a6c68f
- b41fb6e936eae7bcd364c5b79dac7eb34ef1c301834681fbd841d334662dbd1d
- eb5558d414c6f96efeb30db704734c463eb08758a3feacf452d743ba5f8fe662 – packed
- 1f7213a32bce28cb3272ef40a7d63196b2e85f176bcfe7a2d2cd7f88f4ff93fd – unpacked payload
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant Updates



